We maintain strict academic integrity standards, To make sure all work is 100% original.
Our affordable rates make our services accessible to all students. We care about your pockets.
We will elevate your GPA to the roof with our peronalized top notch online class help.
We never compromise on privacy, with state-of-the-art data protection measures in place.


- Liberty University

- DeVry University

- Oxford University

- University of Maryland

- Ashford University

- Strayer University

- Terlaton University

- Stevens University

- Baruch University
Pay Someone To Take My Online Class Help Today!
Why settle for low grades when you can achieve academic greatness with our class help? Trust our Award-Winning Online Class Pros to be your ultimate saviors, providing top class support and unbeatable expertise. We'll turn your online course challenges into a walk in the park, helping you achieve your desire grades with ease. Get enrolled today with our pay someone to take my online course service to avail all the benefits.
Get FREE Online Class Help Trial NOW! Limited time offer! ⏱️
Take Online Class Help Today Without Paying Anything Upfront!
Drop your WhatsApp number to get connected with our online class expert!
Our Pay For Online Class Help Offers:
Our results speak louder than words. Explore our services besides take online class help.

Take My Online Class
- All Classes Help: We take all kind of online degree programs or online college courses on your behalf when you can't manage to complete online courses for any reason.
- Personalized Help: We offer personalize services to address individual needs for their online learning help.
- Expert Tutors: We are a team of more than 70+ tutors who can assist every student according to their courses needs.
- 24/7 Availability: Our team is available around the clock, ready to give you updates and online class support.
- Lecture Attendance: We attend online lectures and complete discussions on your behalf, making sure you don't miss anything.
- Assignment Completion: From start to finish, our pay someone to do course online team will take care of everything.
- Flexible Assistance: Either you need help with self pace courses or any custom help we are pretty flexible with that.
- Smooth Process: Our process is quite easy and smooth, You will be assigned an individual tutor for your online class assistance.
- Academic Success: You can put your trust on us to succeed your online classes, helping to get an A/B grades only.
- Privacy Matters: Your identity will always be hidden we provide 100% secure environment for online classes for students.

Take My Online Exam
- Take My Exam: Having challenges preparing for online courses exams? Don't worry you have come to the right place.
- Personalized Exam Help: We customize our help for your needs, either you need help with certification exams or college/university exams.
- Qualified Exam Takers: We hire top graduates from top universities who can ace any classes or exams and end up bringing your desire results.
- 24/7 Exam Support: Don't take stress if you need urgent help with your exams we've got your back just send us instructions and see the magic.
- Proctored Exam Handling: Scared of online proctored exams? Relax! All you have to pretend you are doing the exam meanwhile our tutors will ace it for you.
- Timely Submission: We submit all the exams on time or even before time making sure all the questions are completed and nothing left behind.
- Flexible Exam Solutions: We are flexible with take my online exam help. You can schedule or reschedule exams at anytime if you get in emergency.
- Improvement Guaranteed: You will see an A or 90%+ in your exams results. We take numerous exams daily hence it has made us God of exams.
- 100% Top-Privacy: We understand your privacy concerns this is why we use hidden security bypassing techniques to save your identity.
Subjects We Provide Online Course Help With:
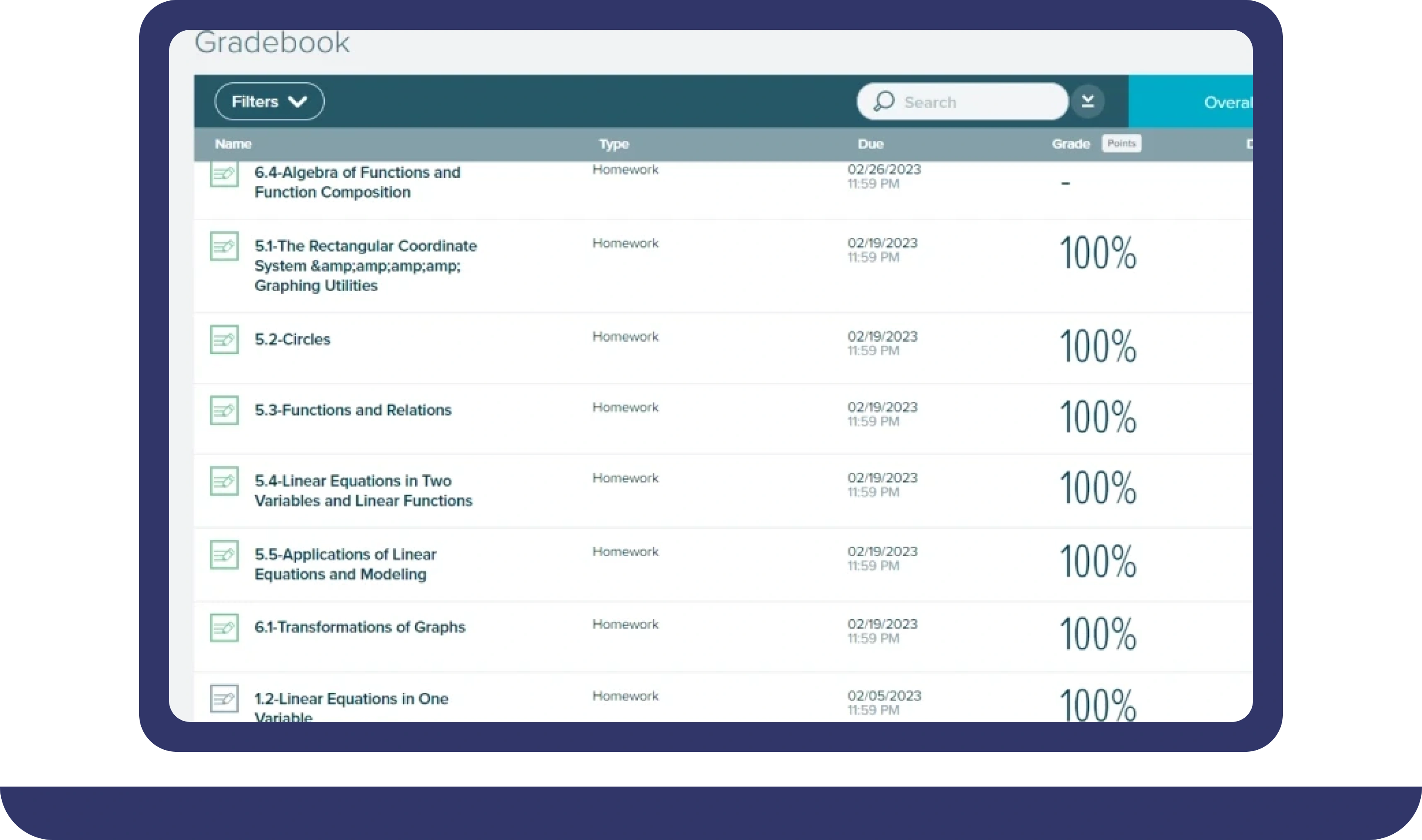
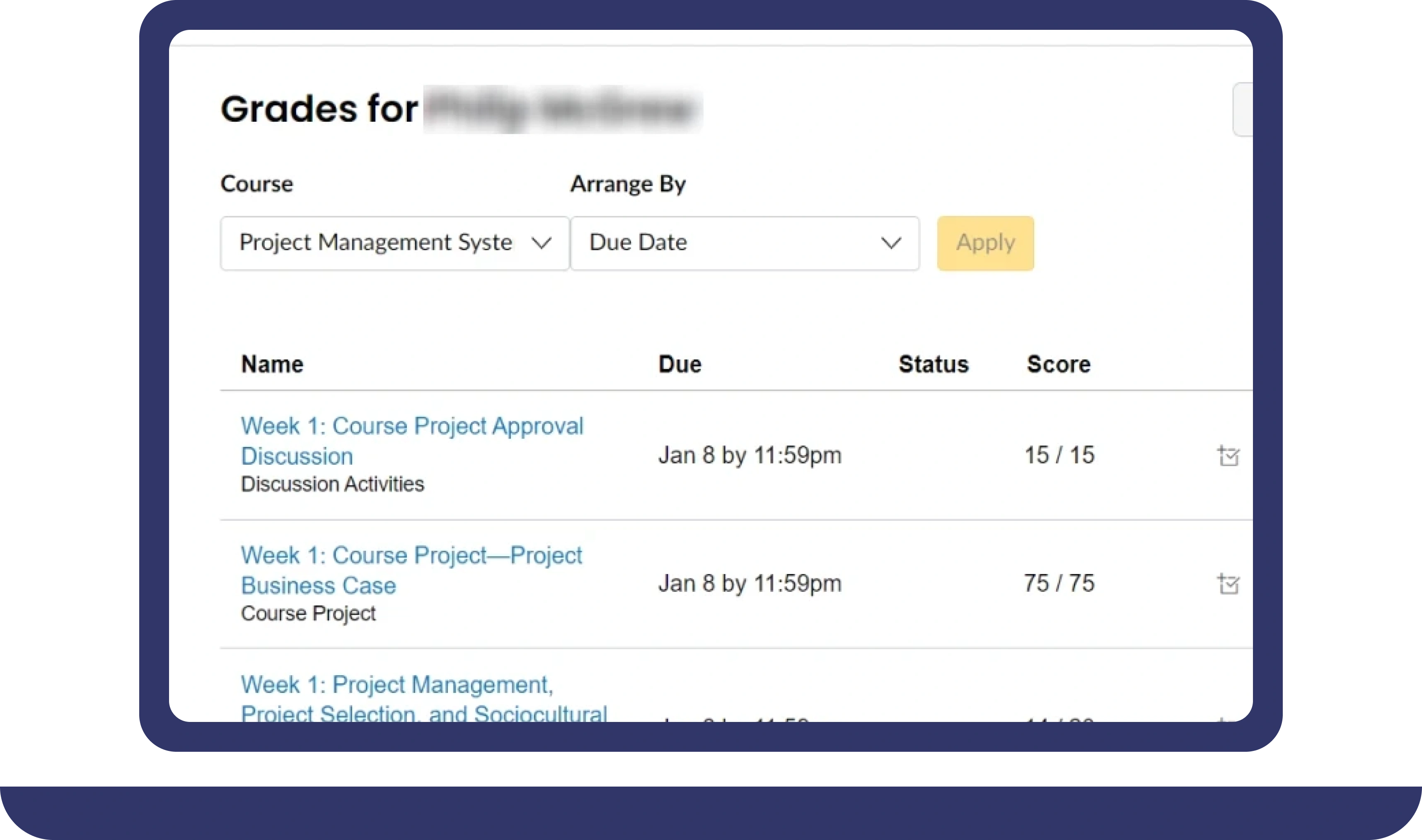
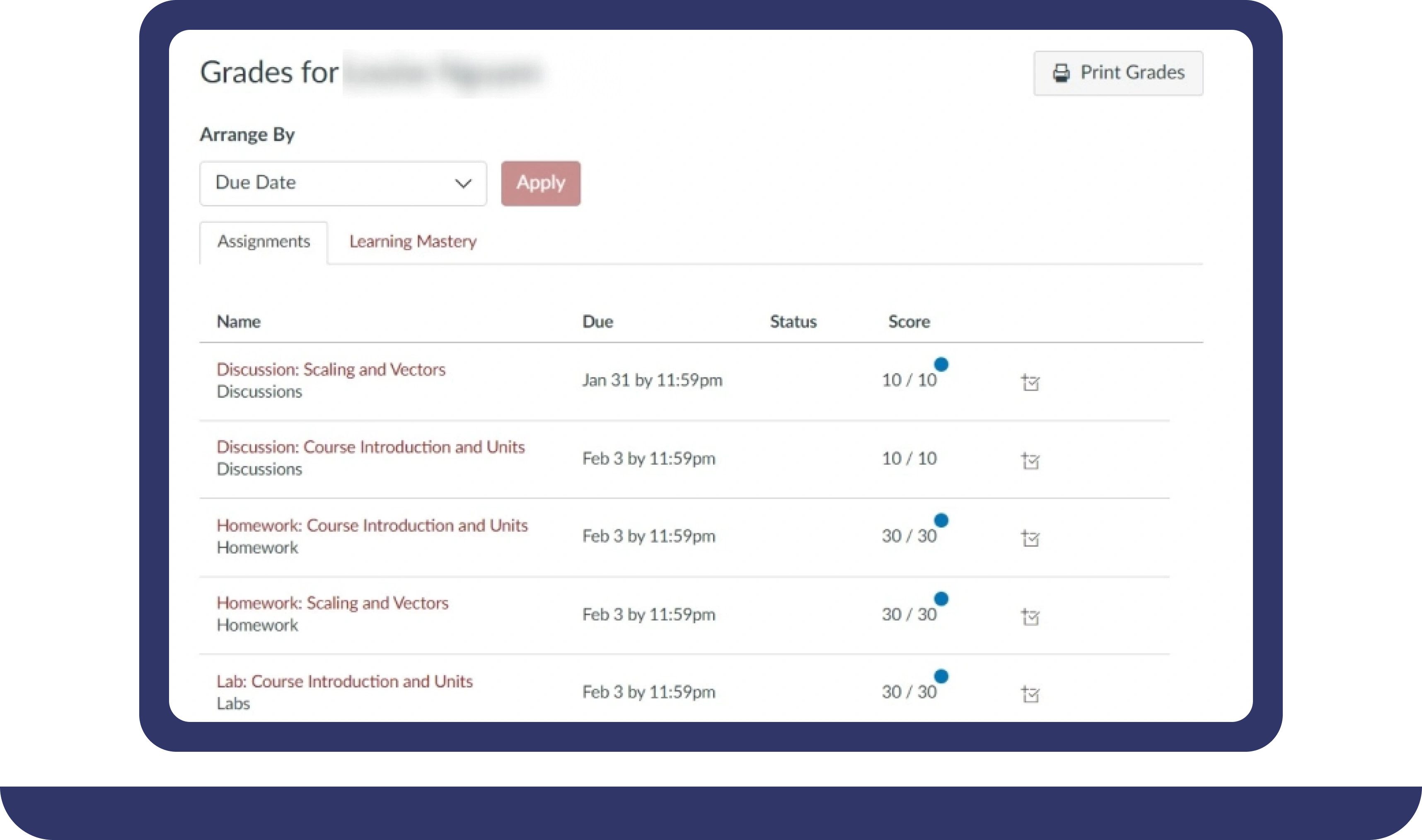
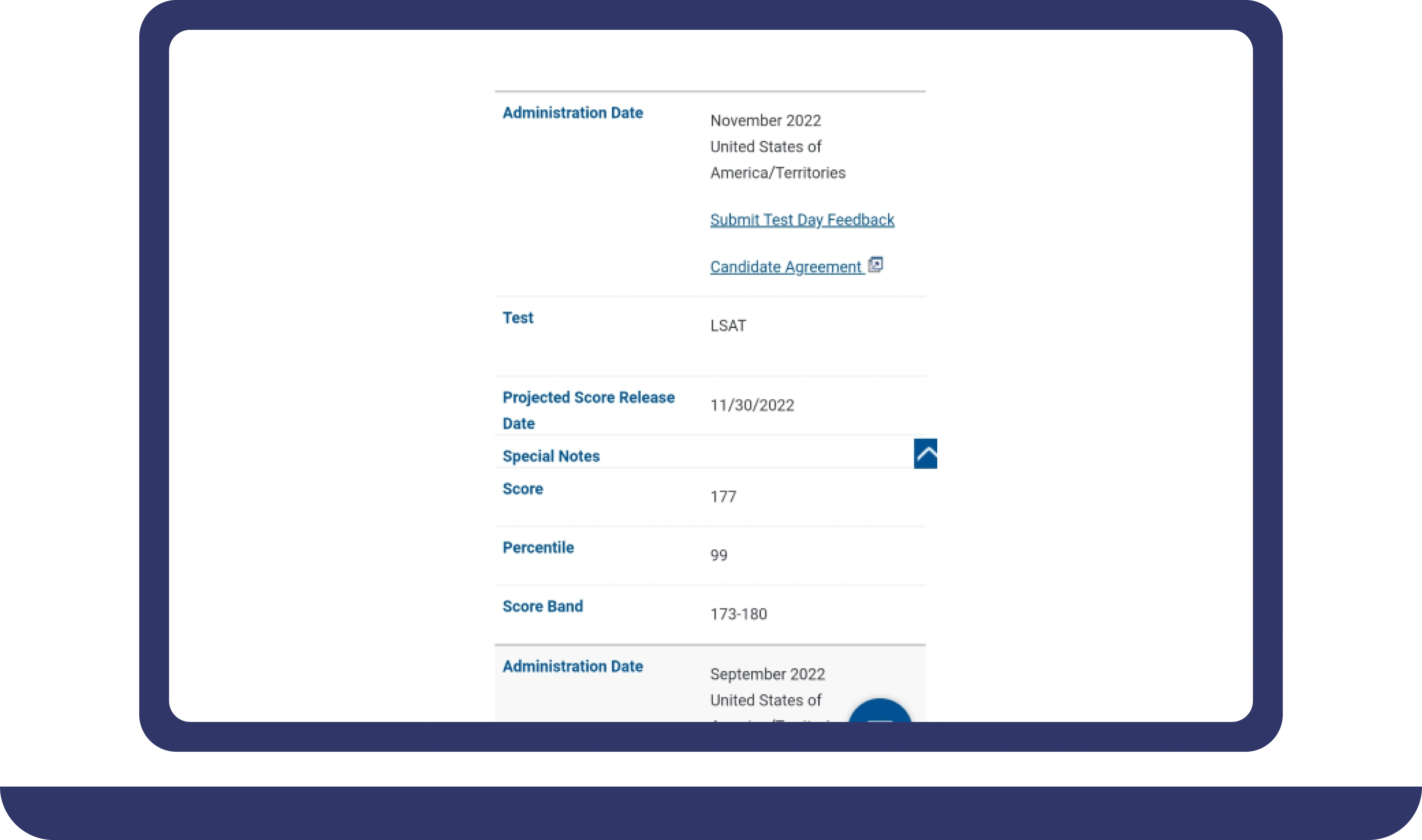
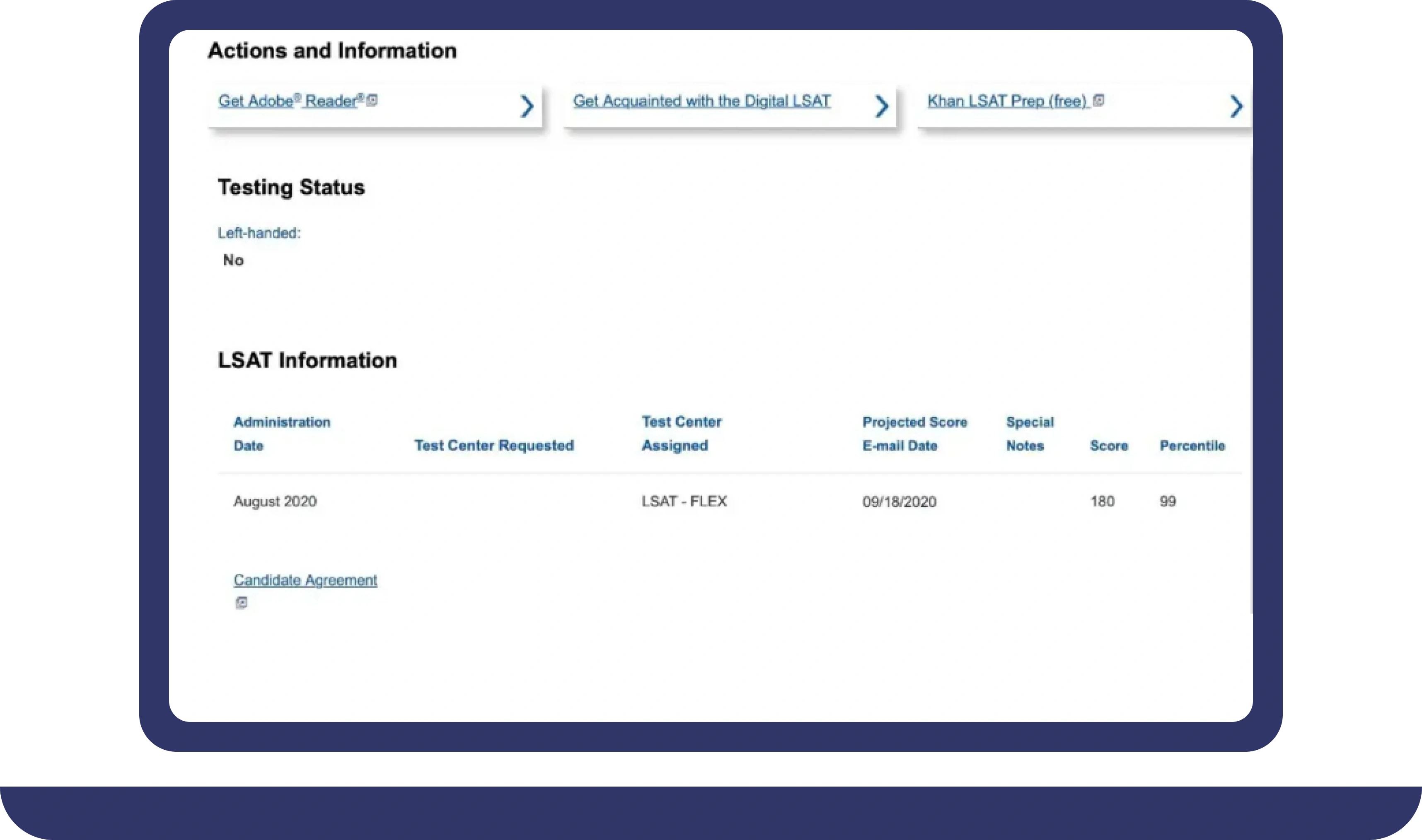
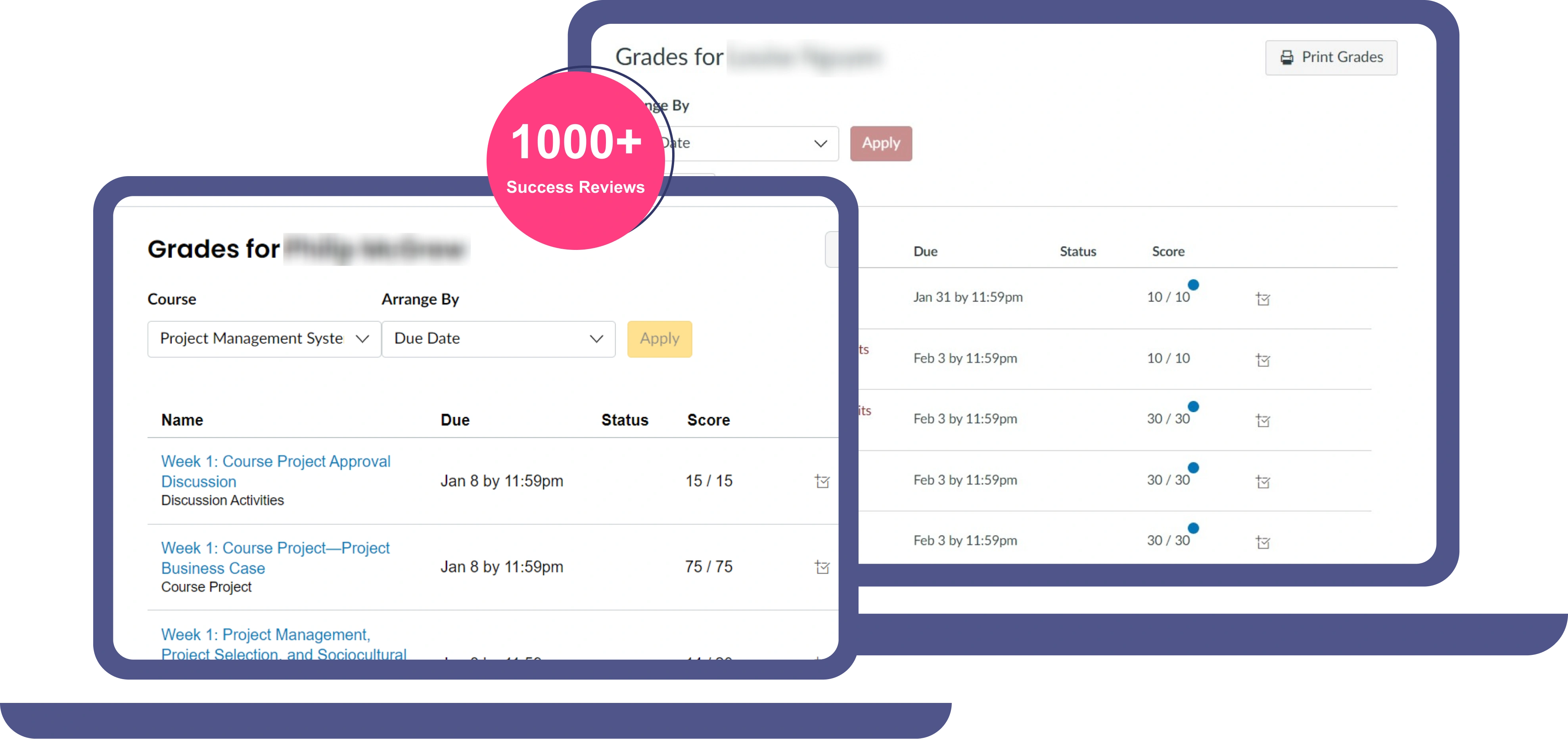
Pay For Grades in My Online Class Success Stories
Why IWantOnlineClassHelp?
- A 7 Days Free Trial Help (Zero Payment)
- B Live Chat for Instant Assistance
- C No Upfront Fees, First Get Your Work Done
- D 1-on-1 Custom Online Tutoring Help
- E USA Based Trusted Service For All Americans
- F Guaranteed High Passing Grades

100%
Trusted

Can Someone Take My Online Class For Me? Reasons Why You Should Hire Us!
Do you ever feel like you're running out of time? Between work, family, and other responsibilities, it can be tough to keep up with your online classes. That's where getting some extra help can make a big difference.
Hiring the best online class helpers or experts can free up your schedule and take a load off your mind. Our professionals online class helpers know their stuff and can tackle your online coursework, exams, or assignments on your behalf. They'll work hard to earn you solid A or B grades, giving your overall performance a nice boost.
Maybe you're struggling with a particularly tough class or subject area. Rather than stressing out and falling behind, you can let the experts handle that difficult online course for you. That way, you can focus your energy on the other important courses where you really shine.
Why consider paying someone for online class help, you might wonder? Well, it's smart for several reasons:
1. Not Enough Time
Ever feel like there aren't enough hours in the day for online university courses? Hiring best online class help frees up your time for other important stuff.
2. Need Extra Help
Our pros know their stuff. They take your online class, exam, or homework on your behalf and score an straigh A grade.
3. Too Much Stress
Online classes, assignments, exams – they can be overwhelming. Getting help takes the stress off your shoulders and makes studies a bit smoother.
4. Want Good Grades
Our experts can give your grades a boost. They've been around the academic block and know how to improve your grades.
5. Other Important Courses
Let's face it – we're all good at something. Hiring help lets you focus on what you're good at while leaving the rest to the experts.
6. A Tough Class
Struggling with a Subject? Let us handle difficult online courses for you, while you give time to the other more important ones.
7. Work-Life Balance
Juggling work, life, and studies? Online class help can restore balance and make the academic journey more manageable.
So, why not consider getting a bit of support? Hire us now!
Why Do Students Often Say Do My Online Class?
Many college students often seek help with their online classes for various reasons:
Time is precious for busy students, and those online classes can really eat into your schedule. When you're struggling to find enough hours in the day, hiring some online course help can free up valuable time to focus on other priorities. No more stressing about deadlines or falling behind – let the pros handle your coursework while you tackle other tasks.
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, certain subjects or topics just seem impossible to wrap your head around. We've all been there – staring at that difficult homework assignment or exam material feeling completely lost. Rather than jeopardizing your GPA, why not pay for online class help from an expert who really knows their stuff? They can guide you through even the most complex concepts.
For students juggling multiple demanding online degree programs or a heavy course load, that mountain of assignments and exams can start feeling insurmountable. Hiring an online class helper means getting a partner to help you manage that overwhelming workload. They'll ensure no crucial tasks slip through the cracks, so you can stay on top of everything.
1. Time Constraints
Students have busy schedules with part-time jobs or personal commitments. It gets challenging for them to manage online classes effectively. So, they opt for online class help.
2. Complex Subjects
Some students find certain subjects or topics complex. They have difficulty understanding their difficult coursework, exam material, and homework assignments. They seek assistance to ensure top grades and GPAs.
3. Overwhelming Workload
Students taking multiple courses and dealing with a heavy workload may need help managing assignments and exams. You can pay for online classes as a helpful solution.
4. Lack of Resources
Some students may look for online class help if they have limited access to study materials or resources in colleges and universities. This can help them maintain their grades better.
5. Balancing Priorities
Students who struggle to balance their academic and personal lives may seek our help. We take their online classes on their behalf to reduce their stress and workload.
6. Desire for Better Grades
Most students who hire us, seek better grades in online classes, exams, or homework. They often need extra help and guidance with difficult courses they find impossible to pass.
7. Technical Difficulties
Online students may face difficulties When the online learning platform or technology has issues. So, they require instant online class help, so they hire us.
"I want online class help" often arises from a genuine need for support and a commitment to academic success.
We Can Do Your Online Classes For Various University
Making sure that you get your money's worth when you pay someone to help you with your online classes is crucial. Luckily, IWantOnlineClassHelp.com has got you covered with a one-stop shop for all your course needs.
1. Online Mathematics Class
We've got the best math experts to help you with your math homework. Lots of students are taking math courses like CPM, Pearson's MyMathLab, University of Phoenix quant coursework, Capella math online class, or McGraw-Hill math connect. All you have to connect with our experts provide them your logins and wait to see the magick.
2. Online Chemistry Classes
Our chemistry helpers are here to make sure you ace your coursework, whether it's Alex's online chemistry class or any other program from a top university. We know that everyone has different needs, so we use everyday language to give you clear and concise assistance.
IWantOnlineClassHelp focuses on the most important information and presents it in a logical way, using short sentences to help you understand. Our top priority is to help you get top grades and complete your degree successfully, so you can always count on us for help.
3. Management Degree Coursework
Management online degree is a thing now, and many professionals finding a roadblock in their career are opting for online degree programs for management courses. The University of Phoenix is a great university that helps you gain exposure to HRM, Quant, Strategy, Marketing, Law, Finance, Accounting, and many more. Moreover, other online college degree providers such as Devry, Ashford, and Capella have similar programs for online certification. You can pay us for online class help with management coursework and classes. We provide end-to-end assistance.
4. Online Physics Courses
Physics can be pretty tough because there are so many concepts to understand and apply in practical situations. But hey, no worries! IWantOnlineClassHelp has got your back, my friend. They have hired a group of expert assignment helpers who specialize in physics and are ready to guide you with your physics assignments, midterm tests, and online courses offered by universities in the US and the UK. So, if you ever feel stuck with physics, give them a try!
5. Online Nursing Programs
Nursing online programs are widely opted for by students across the US and Australia. Many working professional nurses try to give their careers a stable path with the help of online nursing classes. You can pay for help with nursing classes and see how great we excel at it. We know about the class discussions, quizzes, final quizzes, and writeups required to submit for your nursing coursework and degree.
When exploring your options, be on the lookout for affordable online class help deals or even free self-help courses that could fit your needs. You'll find a wide range of services out there, from general study support to specialized offerings like online coding courses with certificates.
If you're considering paying someone to take your online class, be sure to do your research first. While some services simply provide tutoring or resource assistance, others may offer to complete your work for you – which could be considered academic dishonesty. Proceed with caution, and always verify that any paid helper follows ethical policies.
For students who want to improve their skills through self-paced learning, free online self-improvement courses can be a fantastic option. You'll find virtual classes covering everything from professional writing and leadership development to personal finance and entrepreneurship basics.
No matter which path you choose – individualized tutoring, skills-based courses, or just some general online education support – a little extra help can go a long way toward reducing stress and boosting your confidence.
So if you're feeling overwhelmed by your online classes or degree program, don't be afraid to ask for assistance. Enlist some knowledgeable online class helpers or take advantage of readily available self-help resources. With some support on your side, you can conquer any challenges and earn stellar grades.
At the end of the day, your academic journey is a marathon, not a sprint. By strategically utilizing class help services or self-improvement tools when you need them, you can pace yourself while still achieving your goals. Don't be a martyr to burnout – invest in the online learning support that will set you up for long-term success.












Why We Stand Out
We are all about - Commitment, Consistency, and Results.

50,000+ Orders
Proud to be a trusted source of academic support for thousands of students

10+ Years Legacy
With 10+ years of experience, our journey is marked by milestones & achievements.
150+ Skilled Tutors
Expertise from 150+ qualified tutors to ensure an enriching educational journey.
Our Journey: 1,000 Success Stories and Counting
We achieve growth through accomplishments and quality work. Our academic integrity ensures excellence in grades, online exams, and academic tasks, reflecting our commitment to success.
Avail High Quality Online Class Help Irrespective of Your Academic Level
We understand that students have to manage many things simultaneously. Students at all academic levels face somewhat similar challenges.
This is why we offer online class help to students across all academic levels.
Whether you need class help for a science subject or a law one, we provide professional class help tailored to your needs.
Get Personalized Assistance
We aim to provide class help to all the students who struggle to balance their online classes and other commitments. All you need to do is take online class help from our professional online class takers. They will provide you with the best class help that will cater to your class needs.
Get Linked to Our Professional Class Takers Online
Our team consists of class takers online who are skilled individuals. They have years of experience and expertise in a number of subject matters. They can provide you with a premium quality ‘pay someone to take my online class’ service at discounted rates. Our experts not only attend your classes, but they also participate in discussions on your behalf.
Get Online Class Help Pro Anytime
Many students ask us; I need help with my online class and want to take online class help urgently. Can you arrange an online class for me at short notice? You can avail our ‘take my online class’ service any time. We know students have to focus on multiple subjects all at once.
Therefore, we provide online class help services whenever you want. Our class takers online are available all the time to discuss your concerns. Many students get our online class help pro every day because we do not just claim to provide premium quality ‘online class help for me’ service, our results prove it too.
Take Online Class Help from Top-Rated Class Experts at I Want Online Class Help
The goal of our online class help services is to improve students' academic performance. We aim to assist students in managing their responsibilities effectively and alleviating the stress associated with online classes and exams.
Our team consists of top-rated experts who deliver premium quality class help fast. When you feel you are under the heavy weight of online classes, you just need to contact us and ask; Can you take my online class? And our team will deal with the rest! Whether you have easy online classes to take or challenging online tests or exams, we are here to tackle everything for you. Our ‘take my online class’ service is not only flexible but it is designed specifically to meet your online class needs.
Our ‘Pay to Take My Class’ Service Offers Flexibility
Students often wonder, Can I pay someone to take my online class? Can I take online class help without any hassle? We recognize the challenges of balancing academic responsibilities with other commitments. That's why our ‘pay someone to take my online class’ service is designed to be flexible. Simply reach out to us and inquire, I need help with my online class. Can you do it for me? Once you do this, our team of professional class takers and exam takers will be ready to assist you. With our service, you have the freedom to decide when and how you want your classes taken. Moreover, our ‘pay to take my class' service is available nationwide in the USA.
Get Online Class Help Fast: Reliable Assistance When You Need It
Many students inquire; Can you help with my online class? I have some easy online classes to take but can I hire someone to do my online classes? Is it possible for me to get online class help fast?
Classes, tests, and assignments are often announced unexpectedly, leaving students scrambling to fit them into their already busy schedules. We emphasize their struggle, which is why our online class help is designed to be fast and efficient. Our ‘hire someone to take my online class’ service not only offers instant help but also reliability. You can trust us with your classes and get premium quality service at a discounted rate.
Avail Top-Notch Online Exam Help at Budget Friendly Cost
Online education helps students achieve their academic goals by providing many opportunities from the comfort of their homes. However, it requires students to keep up with never-ending online exams and classes. This is why students often find themselves overwhelmed with online exams and classes across multiple subjects. Although they try their best to manage their academic load, it becomes very challenging to do so without asking an outside source for class help or exam help. This is where we come in. We offer top-notch exam help at budget-friendly prices. Our team of experts provides reliable online class help and exam help. With our affordable rates and high-quality service, you will receive the assistance you need to boost your grades.
Instant Support from Expert Exam Takers
Get instant support and assistance from our expert exam takers any time you want. Our team of professional exam takers provides top-notch services as per your needs. Our dedicated team is available 24/7 so that they address your concerns instantly to give you online class help fast.
Achieve Exceptional Results
One of the main reasons students utilize our ‘pay someone to take my online class’ service is to improve their grades. We have a proven track record of providing A and B grades. You can check our online class help reviews to learn about the experiences of hundreds of students who utilized our ‘hire someone to take my online class’ service. Our objective is to deliver exceptional results and help you excel in your online exams. We also offer a money back guarantee in case our expert online exam takers fail to deliver the promised results.
Affordable Prices for All Students
We recognize the financial challenges that many students encounter. That is why we have designed our ‘help with my online class’ service and ‘online exam help’ service in such a way that students with varying budgets can afford it. We offer competitive pricing options to make our high-quality online exam help accessible to all students across the USA.
Leave Your Entire Course to Our Professional Online Course Helpers
Our ‘take my online class’ service not only alleviates the excessive online class burden, but also provides comprehensive course help. Our team comprises professional online course helpers with years of experience in handling courses for students. Our online course helpers have expertise in various subjects. They will give you the best course help in the entire USA. When you take our online course help, we handle every aspect of your course from attending classes to completing online exams on your behalf. So, if you need online class help or online course help, our top-notch course help is readily available. Browse through our online class help reviews, fill out our form and receive prompt assistance right away!
- Expert assistance from professional course helpers
- Comprehensive course help
- Timely submission of assignments, tests, and quizzes
- Instant course help available 24/7
Get 100% Original Assignments
Assignment writing is an important aspect of online courses because teachers use them to evaluate student’s progress. When you take our online course help, we not only provide assignments on your behalf, but we also make sure your assignments are 100% original. We provide plagiarism-free assignments that adhere to the required standards.
Stay Informed on Important Announcements
Our team of online course helpers are able to manage your entire course perfectly. Our course helpers are trained to handle multiple tasks at once. They attend your classes, participate in discussions, do your tests and quizzes for you. Not only this, but they also keep you updated on upcoming tests and assignments.
Leave Your Online Tests to Our Course Helpers
If you have a test that you have not prepared for, trust them to our experts who have expertise in a wide range of subject matter. We make sure that you score A+ grades in all your tests. Avail our ‘take my online class’ service now and achieve your academic goals.

Start Your Success Story: Easy Steps to Get Started

Order Placement
Placing an order at IWantOnlineClassHelp is easy and hassle-free! Just fill out the order form or call us at +1 (657) 300-3540. As soon as you complete your registration process, you'll receive a confirmation email or text from our support team with your next steps of order.
Payment Confirmation
Confirm your payment as quickly as possible, so we can proceed with the order process. We want to make things easy and fast for you. We accept different secure payment methods like Wire Transfers, PayPal, Card, Zelle, CashApp, and Venmo, so you can choose the method that suits you the best.

Order Review
As part of our commitment to excellence, we'll send you a preview of your order before the deadline. Take a moment to review and, if you want to add something, let us know of any changes. We're here to ensure your complete satisfaction with every aspect of your order.
Revision & Feedback
Enjoy unlimited revisions upon receiving your final ordered version. Our commitment to quality aims for your utmost satisfaction. We value your feedback, and if you're pleased with our online class services, feel free to share it. You can provide feedback by filling out the form or sending an email to: [email protected].

Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, you can pay IWantOnlineClassHelp to take your online class. We are a reliable and legit online class taking service. Email us at [email protected] or fill out the form to get a free quote.
Yes, pay IWantOnlineClassHelp to take your online test. We provide 100% confidential and authentic service with a guarantee of plagiarism-free work. IWantOnlineClassHelp also promises to secure only A/B grades (Class, Exam, Homework, etc) on your online test. So, get started now!
We have a team of 135+ highly qualified and skilled homework experts. They are available 24/7 to provide you with top-notch, high-quality service. Our team of live chat representatives is also available round the clock to assist you with any kind of homework-related query (Class, exam, homework, etc.). Get a free quote
Passing an online exam (Class, Exam, Homework, etc) is now easy with our skilled experts. Hire them and have a stress-free experience meeting your deadlines and exam protocols.
Yes, we prioritize your online security. IWantOnlineClassHelp uses top VPN solutions to verify your identity during class logins, ensuring that access comes directly from your location. Our goal is to match you with a local online class expert. If needed, we use IP masking to protect your location privacy.
Yes, we offer a guaranteed refund policy for your satisfaction. If you're not happy with our service, we promise a hassle-free refund. Your peace of mind is important to us.


